You wouldn’t have expected Disney to join the cryptocurrency craze, but that’s exactly what has happened. The beloved mass media and entertainment company, known for its classic animated films like Aladdin, The Lion King and most recently Moana, is now trying to carve out a space in the blockchain world as a cryptocurrency-agnostic smart contracts platform.
If you’ve not been keeping abreast of developments in the cryptocurrency world, smart contracts are arguably the single most valuable use case for blockchain technology. It’s a common misconception that Bitcoin or blockchain is money. What it actually is is programmable protocols, a protocol that can be tailored and tinkered to suit a variety of objectives.
This programmable nature is what lets developers create decentralized applications that can work as auto-enforcing negotiations between two (or more) parties. The smart contract can be programmed to stipulate a variety of conditions that must be satisfied, following which payment and services are delivered.
So how does the once Disney-run, now Dragonchain Foundation owned project plan to work with this, and what are their plans to employ smart contracts?
What Is Dragonchain?
Research and development of the Dragonchain project began in 2014. It started out as the Disney Private Blockchain platform and was released as open-source. In 2017, the Dragonchain Foundation, a non-profit organization, was launched and the Dragonchain platform, as we know it today, was born. The foundation was created specifically to maintain ownership and responsibility of the open-source code. Since then, it has been taken over by the Dragonchain Foundation, a non-profit organization.
Developing smart contracts is not very user-friendly or convenient. Currently, it is limited to those with some programming ability. Considering that smart contracts will be put to use in mostly non-technical fields, it is necessary for a platform to be as approachable and intuitive as possible. Furthermore, currency restrictions limit the practical application of smart contracts in the real world. Dragonchain’s feature of being able to create smart contracts, with or without currencies, and its support of multiple currencies gives it a broader appeal.
This is what Dragonchain aims to do: create a secure, flexible and developer-friendly platform that shares data and smart contracts, with attention to interoperability.
Dragonchain is very business-oriented, striving to make integration of business applications simple, while also focusing on currency agnosticism, protection of data and the support of different currencies. Such a smart contract is the ideal that all platforms of this nature should work towards.
Now, there are a number of companies attempting to broaden data and smart contract sharing capabilities. The #1 player in this space, Ethereum, is itself limited in its capabilities. More specifically, it gives us a tantalizing taste of what the ideal smart contracts platform would like.
Can Dragonchain be a suitable alternative to more established platforms? Is there something that distinguishes it from the countless players in this space?
How Is Dragonchain Unique?
The Dragonchain platform’s goal of being the most convenient location on which to develop smart contracts shows in its distinguishing features.
On Dragonchain’s Github page, the team has stated their guiding principle quite clearly:
The decentralized and singular approach to blockchain implementation is sometimes at odds with the real business need to protect information and control business processes.
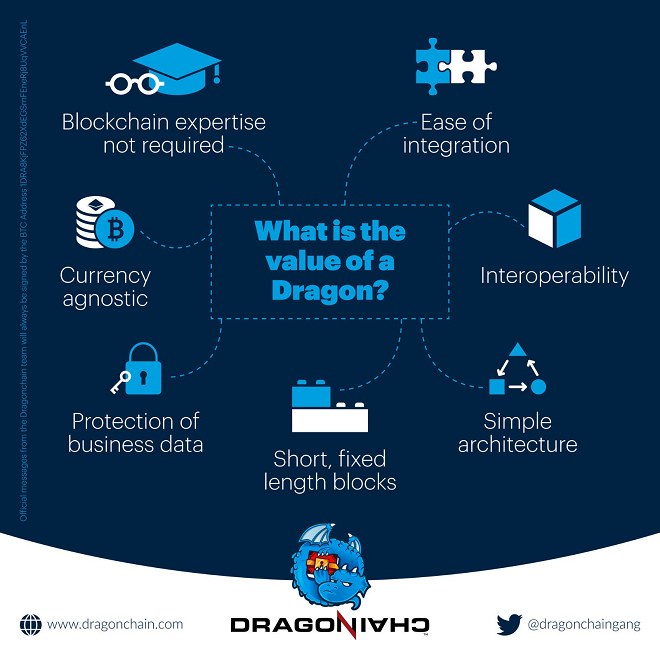
One of the ways in which the Dragonchain team is circumventing this problem is by supporting several languages for the development of smart contracts. This includes Java, C#, Python, Go and NodeJS. This support will attract more developers, and, when it comes to cryptocurrencies, greater inclusion has a strong correlation to success, provided certain other criteria are met. The platform itself is scalable and server-less, with built-in protection of business data.
Dragonchain will also create a marketplace for the sharing and selling of smart contracts. Developers will be able to showcase their work and monetize it. This ecosystem will encourage developers to build better applications, as it is something of a portfolio and business network spot.
In fact, Dragonchain calls it an Incubator, a place where subject matter experts, qualified vendors, pre-built libraries of smart contracts and incubated projects are present to help businesses fully utilize the flexibility of smart contracts. In a nutshell, businesses will have access to all the resources they need to conduct transactions.
The DragonFund Incubator is worth describing in detail. An incubator is a service that helps up and coming businesses or startups grow through training, exposure and consultation. Dragonchain’s incubator is doing the same, except it’s focusing on smart contract projects and services. The stakeholders in the ecosystems can visit the marketplace to compare, evaluate and support various projects. They will have communication access to legal, technical and financial experts who can advise non-technical individuals in their areas of expertise. This makes it easier for businesses to get involved with blockchain and smart contract projects.
Dragonchain also has a patent pending on tokenized micro-licenses. This micro-license will let users interact with the platform. Currently, there isn’t much information on this, but we’ll be sure to update this article when it does arrive.
Dragonchain’s desire to build a self-contained ecosystem is commendable, as it seems to genuinely look out for the interests of all involved parties. They are hoping that their approach will result in a faster speed to market, lower development costs, and higher speed and security.
How Does Dragonchain Work?
There are 3 services offered by the Dragonchain platform. First is the platform itself, where developers can create contracts in a variety of languages, in a server-less and scalable environment. Business data is protected and all contracts have the full access to Amazon Web Services.
Next is the DragonFund Incubator which, as we mentioned, can help blockchain projects grow through crowdfunding.
Lastly, we have the marketplace, which is an ecosystem of subject matter experts and monetized smart contracts which can be reused by businesses.
It is the Dragon token (DRGN) that will allow interaction on all of these services. There are 3 main stakeholders in the Dragonchain network: founders, developers and the community.
The founders can use the Dragon token to incubate their project. The developers can use the tokens to spin up nodes, provision smart contracts or become involved in the smart contracts marketplace. As a member of the community, you can use the token to gain early access to projects, in the same way that crowdfunding works today.
The Dragonchain Team
Dragonchain is supported by a 7-member team with expertise in software architecture and cloud deployment.
The company was founded by Joe Roets, who is also the CEO. He has over 20 years of experience in software architecture, specifically scalability and security. He has also launched and led multiple startups from as far as back as the mid-1990s.
Ellen Quenin is the the Dragonchain Foundation Founder and President as well as the VP of Strategic Partnerships. She played a pivotal role in making this project open source. She also has 7 years of experience at the Walt Disney Company and has worked with Amazon Payments, GE healthcare and LexisNexis.
Paul Sonler is the CTO and has arrived from Disney, where he worked on cloud deployment and photopass modernization. He was involved in the early development of Dragon and has over 20 years of software engineering experience. He is a graduate of Carnegie Mellon University.
George Sarhanis is the co-founder and CBO. He has worked as the Marketing Director of Echospace Technologies and has previously founded a startup. He has over 17 years of experience in business management.
Overall, the team has a wide range of experience evenly distributed across technology, business, marketing and strategy.
The Dragonchain Vision and Roadmap
Dragonchain strongly believes that blockchain will disrupt industries and that the world will shift towards decentralized environments, as stated in their whitepaper.
They are hoping that their platform will appeal to a variety of businesses, particularly non-financial ones. The platform allows for monetary models to be applied after integration,which will let businesses use real-time data to best gauge which monetary model to apply. They aim for an adoption of standards, no base currency, ease of integration, protection of business assets and ease of integration.
Dragonchain’s roadmap clearly communicates the path the company wishes to take in their quest to make smart contracts for businesses easy. Their goals are also telling of their intentions to make the whole process easier – in July 2018, they plan to launch the Dragonchain Foundation Developer Academy Pilot Program, which will conduct smart contract development workshops and training. In August 2018, they will launch the marketplace promotion and partnerships.
The incubator itself will launch in September 2018. Over the year, they will establish full support for Amazon AWS, Google Cloud Environment and Microsoft’s Azure.
How Have They Been Performing?
At a total market cap of over $660 million, there are about 238 million Dragons in circulation (information accurate at time of writing). The maximum supply will be 433 million coins. This is based on the ERC20.
The public sale began on October 2, 2017 and ended on November 5, 2017. 55% of the tokens have gone to the public, 20% to the team, 10% to the foundation, another 10% into Dragonchain’s reserves and the remaining 5% into the DragonFund Incubator.
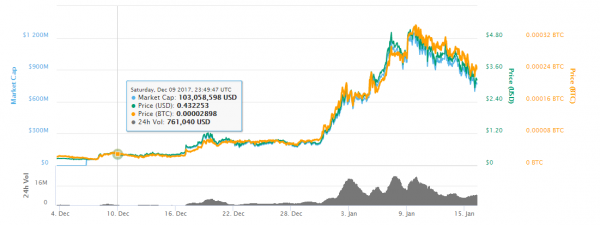
At the time of writing, the coin is now valued at roughly US$2.70. They spiked in value at the beginning of 2018, hitting a peak market cap of $1.2 billion.
Competitors and Challenges
Dragonchain is up against the whole field of smart contract players which, of course, includes Ethereum. Ethereum is a part of the Ethereum Enterprise Alliance, which is a collection of top businesses. NEO is another smart contract platform with significant influencers backing it.
However, Dragonchain’s support-all nature is an indication that they do not want to compete with other coins. Rather, they want to create the best possible environment for projects and funders. They are not competing, but aiding. They allow developers to use whatever tools and platforms they like to create applications, which they can then sell on the Dragonchain marketplace with no restrictions in currency or blockchain.
This open-mindedness could possibly make them a long-term survivor and something of a playground for smart contracts. However, if one or the other smart contract platforms becomes the only dominant player, say Ethereum, then there is little reason to use a platform like Dragonchain.
Still, the idea is tempting. We’ll have to see how 2018 pans out.
How to Purchase and Store Dragonchain
It is not possible to buy DRGN with fiat currency, so you’ll have to exchange it for another cryptocurrency. It is listed on a number of exchanges.
It’s best to exchange Bitcoin or Ethereum for DRGN. Once you’ve done that, head over to the Kucoin Exchange. Send the ETH or BTC to Kucoin and make an exchange for DRGN there.
Final Thoughts
In order to encourage growth of the smart contracts space, developers will need incentives and businesses will need to be eased into smart contract use. Dragonchain hits the mark on both of these. Dragonchain’s open-source nature and willingness to let different currencies and blockchains cooperate is something that should be appreciated, even if it’s unsure whether blockchains will work like this in the future.
Their team is experienced, their roadmap is solid and their goals are noble but realistic. For that reason, Dragonchain is one to keep an eye on in the upcoming months. It could just become a sudden contender in the smart contracts niche.